The petroleum refining industry plays a significant role in the economy. Most of the world's transportation systems and industrial, residential, and commercial activities are powered by petroleum-based products. Although refineries can be found almost everywhere globally, the United States is the world's largest crude oil refiner, with 126 active petroleum refineries that can handle over 18 million barrels per day as of January 2021. These refineries primarily produce gasoline, jet fuel, distillates, lubricant base oils, amongst other products. The Port Arthur Refinery in Texas is one of the country’s largest refineries, with a daily refining capacity of over half a million barrels. The Baytown refinery and the Garyville refinery are also major petroleum product producers in the U.S.
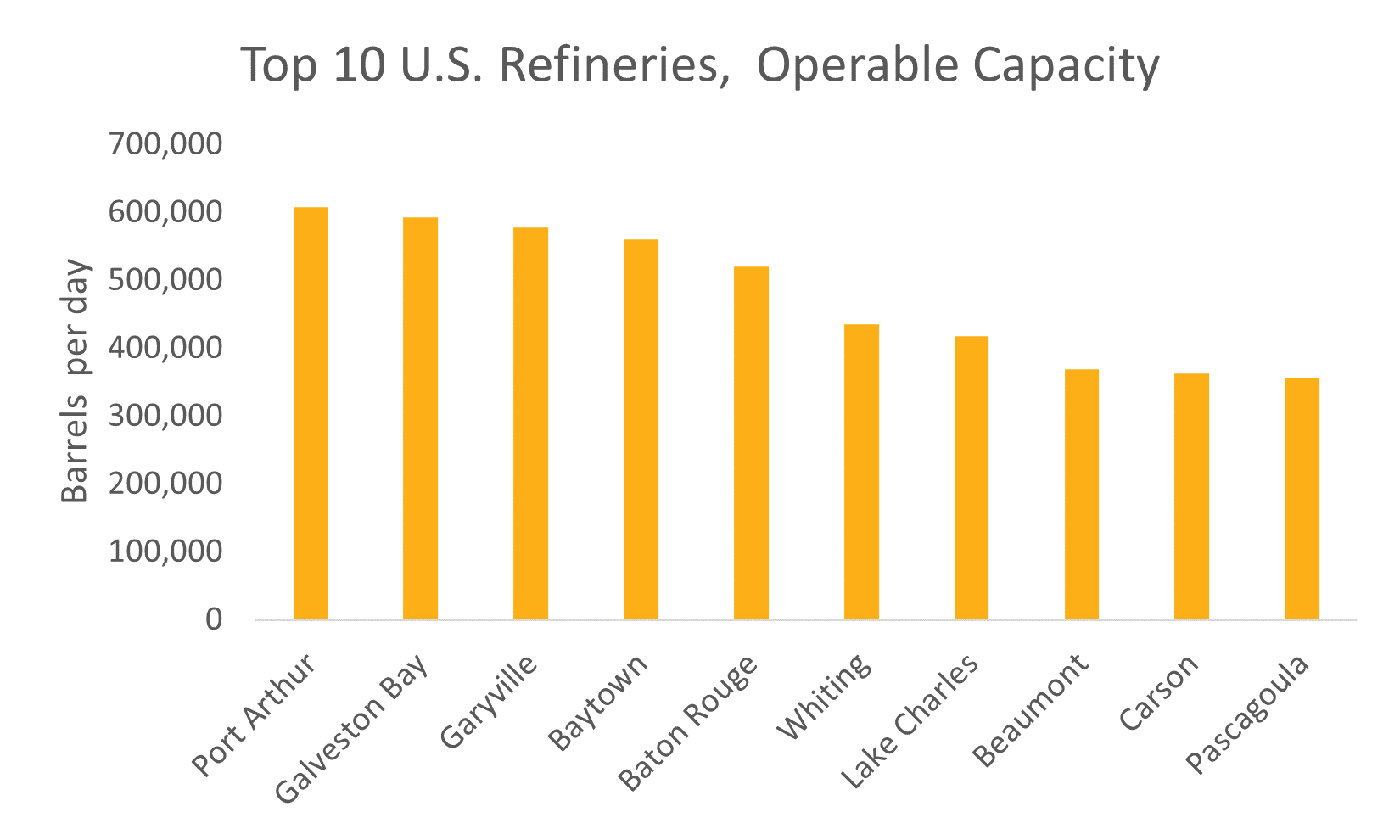
Source: U.S Energy Information Administration
Health and Material Impact of Air pollution
Although refineries are an important element within the U.S energy infrastructure, they also emit hazardous and toxic air pollutants, including particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), and sulfur dioxide (SO2), which can be detrimental to the environment and human health. These air pollutants, also known as non-greenhouse gas air emissions, can cause a number of health issues, including respiratory problems and congenital disabilities, with some being even carcinogenic. While the level of hazardous air pollutants emitted by U.S refineries has generally decreased over the years, they continue to pose health risks to surrounding communities. Recently, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has identified over 70 refineries with “High Priority Violations” of the Clean Air Act (CAA). Moreover, several refineries were imposed state or federal penalties ranging from USD 4,650 to USD 4,342,660 between 2019 and 2021.4
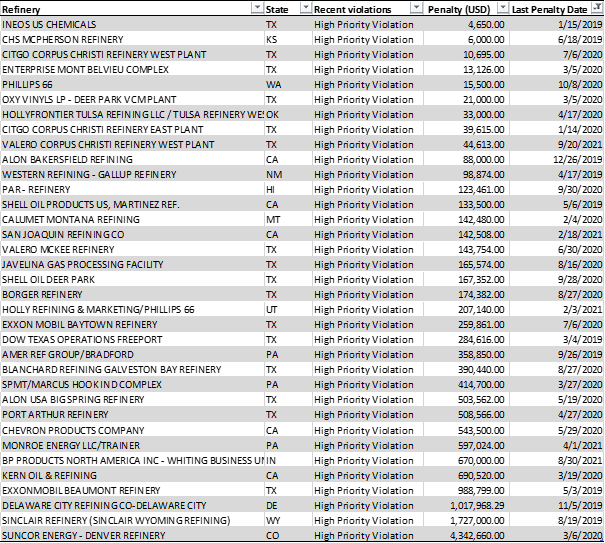
Source: U.S Environmental Protection Agency
So how can investors assess the readiness of petroleum refiners?
Managing air pollution can be costly for companies, and investors need to know this. Notably, they should make sure that the companies they invest in have plans to reduce emissions and are prepared to comply with potential upcoming regulations. Sustainalytics’ ESG Risk Ratings framework can support investors to evaluate petroleum refiners and their ability to manage air pollutants. This can be done by assessing the material ESG issue Emissions, Effluents and Waste. Specifically, investors can examine to what extent petroleum refiners manage their Non-GHG Air Emissions and assess the quality of a company's programs to reduce air pollutants. For instance, examining all the petroleum refiners assessed by Sustainalytics, we observe that only 3% have a strong program to manage non-greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, while 39% have an adequate program, 33% have no data or disclose limited information about their programs to manage air pollution. Having the ability to identify companies that mitigate risks relating to air emissions can help investors make informed decisions.
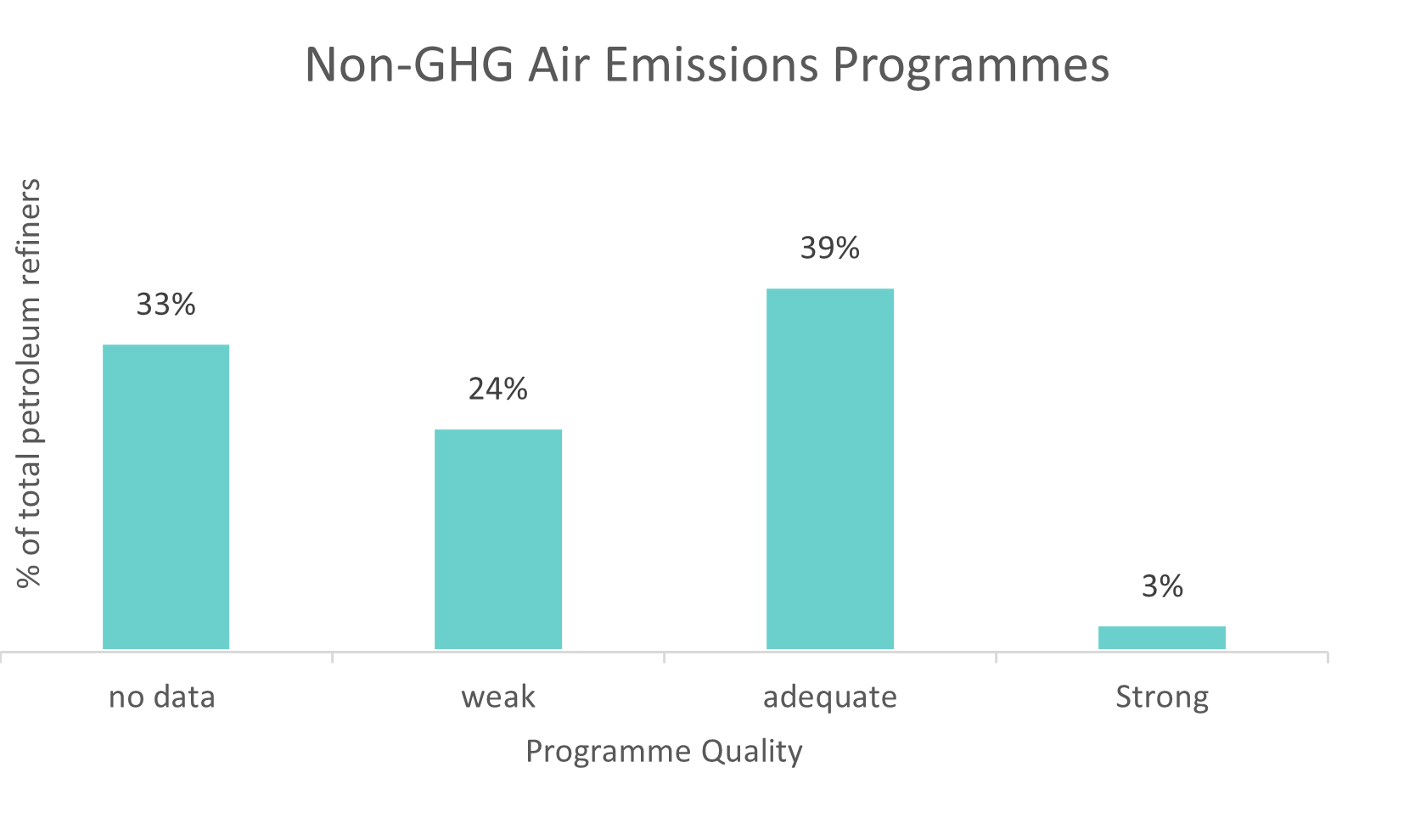
Source: Sustainalytics
Despite improvements made by the petroleum refining sector in the U.S in recent years, the emission of toxic substances into nearby communities continues to pose a severe public health risk. As a result, the monitoring and regulation of petroleum refiners and other petrochemical facilities may likely become stricter in the near future. Moreover, the material risks relating to breaching existing air emissions regulations should not be overlooked. Over the past 20 years, the EPA has entered into 37 settlements with a number of petroleum refiners, with settling companies agreeing to invest over USD 7 billion in control technologies and pay civil penalties of more than USD 116 million.5 Thus, a strong understanding of how companies manage the risks associated with air pollution is critical for those who are interested in investing in the petroleum refining sector.
1. Administration, U.S Energy Information. [Online]
2. EPA. What are Hazardous Air Pollutants? [Online] https://www.epa.gov/haps/what-are-hazardous-air-pollutants.
3. Report, 2017 NEI Interactive. [Online] https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-inventories/2017-national-emissions-inventory-nei-data.
4. Facility, EPA - Enforcement and Compliance History Online - Air. EPA - Enforcement and Compliance History Online - Air Facility Search. [Online] https://echo.epa.gov/.
5. EPA, Petroleum Refinery National Case Results -. [Online] https://www.epa.gov/enforcement/petroleum-refinery-national-case-results.

.png?Status=Master&sfvrsn=57d9699_1)
.tmb-thumbnl_rc.png?Culture=en&sfvrsn=12471767_1)


