Described as the “last best chance to get runaway climate change under control", the COP26 summit resulted in numerous pledges made by countries and entities on reducing carbon emissions, environmental restoration and investing in green initiatives. While targets and pathways vary, it underscores the task ahead to limit global temperature rise.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), nearly 40% of global carbon emissions originate from the construction process and operation of buildings.1 At the same time, a Marsh McLennan report anticipates global construction output to grow 42% by 2030.2 These figures suggest that the real estate development industry may face pressure to find opportunities to support COP26 objectives.
As an innovation in the industry, mass timber construction emits significantly less carbon than traditional concrete and metal structures, while modular construction ensures usability across many building types. This article reviews some of the concerns over structural strength, fire safety, regulatory compatibility, cost savings and the sustainability of increased forestry. It then examines current mass timber buildings and projects and looks at their viability as an alternative material for the future.
What is Mass Timber?
Origins of mass timber construction can be traced back to Austria and Germany in the 1970s and have spread across Europe in the 1990s with the development of cross-laminated timber (CLT); North America has become an emerging market over the past several years. CLT describes a category of engineered wood products made by compressing and gluing three layers or more of millimeters-thick wood together, allowing for off-site manufacturing and use as building components, such as large wood panels or load-bearing structural columns and beams, secured in place using fasteners or adhesives. Mass timber can be built to similar strength ratings to concrete and steel while weighing significantly less.
A substitute for carbon-intensive steel and concrete, mass timber can be used as supplementary or replacement material to steel and concrete builds or in a full timber frame structure. For contractors, on-site assembly is often completed with simple hand tools and minimal heavy equipment.3 The timber itself can keep carbon out of the atmosphere as long as it is not burned or destroyed. With the UN projecting global urban populations to increase by almost 50% by 2050,4 mass timber can be an alternative approach to help limit global temperature rise in the face of increased demand for buildings.
Cost Advantages
While costs will vary depending on the region, application, size, and scope of each project. In Europe, CLT is estimated to cost between USD 2,300 to USD 2,900 per square meter,5 which is higher than comparable concrete components. In the US, a 2021 study by US architectural firm LPA Design found that CLT would cost approximately USD 10 more per sq/ft than a conventional steel and concrete building in a commercial office application.6 Despite the cost delta, this gap can be overcome through cost savings elsewhere in the project. Incorporating more modular components in designs over bespoke components can also further reduce costs. Global CLT production capacity in 2020 was estimated at 2.8 million cubic meters, with Europe and North America accounting for the largest proportion at 48% and 43%,7 respectively.
CLT building components can be mass-produced and pre-assembled off-site before site delivery, reducing development lead times and labour costs. As CLT components weigh about 30% less than concrete equivalents, additional savings can be found via lower transportation costs, creating smaller building foundations, reduced crane and heavy equipment rental needs, lower interior finishing costs and less material waste, which would offset higher initial costs.
Structural Strength
Mass timber’s production process of compressing wood layers and chemical treatment gives components their tensile strength. Being only a fraction of the density of concrete and steel with comparable strength ratings means mass timber products are lighter and have higher strength-to-weight ratios. This allows for smaller building foundations whilst being able to support loads comparable to steel components.8 Other benefits to mass timber include resilience against lateral loads without distorting or breaking, such as high winds and earthquake-related forces,9 which are important characteristics for buildings in seismic zones or at risk of high wind buffeting.
Fire Safety
While wood is perceived as flammable material, mass timber is inherently fire resistant. This is achieved as the outer surface chars when exposed to fire, acting as insulation and delaying the effects of heat on the structural core, slowing the progression of a fire.
External tests with CLT panel walls have seen it withstand 1,800-degree Fahrenheit heat for over three hours, well beyond the two-hour rating required in building codes.10 The ICC set fire resistance ratings as part of the 2021 IBC mass timber building-related amendments and the International Fire Code, further legitimizing mass timber as a safe building material.
Regulatory Compatibility
Since 2015, the International Building Code (IBC) has included provisions for mass timber materials being used in buildings. In 2018, the International Code Council (ICC), a global building safety standard, had voted to recommend mass timber products, which culminated in the 2021 IBC code, which introduced 14 amendments, including the introduction of three new construction types for mass timber buildings that allow for up to 18 floors.11
Eurocode 5, an EU design standard that governs building design and engineering using timber, was updated in 2019 (the first major revision in 15 years) to include CLT material and load-bearing standards. The states of California, Oregon, Washington and Utah, plus cities like Denver and New York, have amended their building codes to allow mass timber projects to build taller.
Increased Forestry Demand
A misconception is that mass timber demand would require harvesting larger trees and cause deforestation. With wood being a renewable resource, it can be regenerated using sustainable forest management practices. Mass timber generally uses younger, fast-growth trees (such as spruce) smaller than 11 inches in diameter on average.12 Combined with responsible forestry practices, it leaves old-growth trees untouched. According to the United Nations’ The State of the World’s Forests 2020 report, some of the largest uses contributing to global deforestation are agriculture (commercial and local) and mining, accounting for 73% and 7%, respectively.13
Across the EU, member states have enacted national forestry legislation to ensure sustainable forestry, which increased forest coverage in Europe over the past 30 years.14 In the US, a 2018 US Forest Service report found that 67% of the country’s forest land was legally available for harvesting, but less than 2% saw any tree removal each year.15
Building Examples
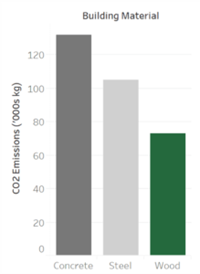
*Graph: CO2 emissions from equivalent large office building designs. https://mantledev.com/insights/embodied-carbon/mass-timber-carbon-impact/ *
 Ascent Tower (Milwaukee, WI): Developed by New Land Enterprises LLP and slated for completion in the fall of 2022, the 259 unit, 25-story residential tower is reported to be North America’s tallest hybrid timber building at 284 feet tall. The hybrid timber and concrete structure (the latter material for its foundation and core structural stability) received a federal grant from the US Forest Service to assess mass timber’s capabilities in meeting US building code regulations. New Land Enterprises states that using timber beams, slabs and columns will offset enough CO2 to power 1,200 homes each year versus using concrete.16
Ascent Tower (Milwaukee, WI): Developed by New Land Enterprises LLP and slated for completion in the fall of 2022, the 259 unit, 25-story residential tower is reported to be North America’s tallest hybrid timber building at 284 feet tall. The hybrid timber and concrete structure (the latter material for its foundation and core structural stability) received a federal grant from the US Forest Service to assess mass timber’s capabilities in meeting US building code regulations. New Land Enterprises states that using timber beams, slabs and columns will offset enough CO2 to power 1,200 homes each year versus using concrete.16
80 M Street (Washington, D.C): Commissioned by Columbia Property Trust, 80 M street was originally built as a traditional steel and concrete office building in 2001. Demand for adding further density to existing business districts whilst adhering to municipal building codes (which limited building heights to 130 feet tall) and foundation weight constraints, demonstrated mass timber’s ability to be an added main element into an existing build. Despite adding two additional floors and 105,000 square feet of space to the seven-storey structure, the inherent lightness of mass timber did not require additional foundational reinforcement, while its prefabricated components avoided significant on-site disruptions for existing tenants. The addition project is scheduled for completion by mid-2022.17
Sara Kulturhus (Skellefteå, Sweden): Built by the architectural firm White Arkitekter, Sara Kulturhus is a cultural centre with a hotel on its premises in Northern Sweden. Completed in September 2021, this 323,000 square foot structure contains exhibition halls and stages, a library, and a 20-storey hotel. Save for the underground structure and some load-bearing steel girders in the foyer, the rest of the structural components were made from mass timber harvested within 30 miles of Skellefteå and milled into prefabricated components, with the hotel portion constructed by stacking self-supporting boxes in place. The timber used is projected to store about 6,000 tons of CO2, with solar panels and efficient energy systems further minimizing its carbon footprint.18
Mass Timber in the Future
While mass timber may not be suitable for every project, it can play a huge role in the future of buildings. UNEP’s 2020 Emissions Gap Report identified that buildings and cities are among the six sectors that will play a key role in limiting temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius,19 especially as timber sequesters carbon and is renewable. Modular designs to enable off-site assembly, reduced on-site construction time, lighter-weight components and less material waste can realize cost savings. The ability for mass timber components to be reused is another major positive, as the concept of transitioning to a circular economy gains traction. We anticipate that mass timber will grow in appeal to consumers and developers over the next several years. Drivers include further global building code changes that allow for taller wood construction projects, technological advances in material and engineering solutions to allow for more cost-effective and widespread adoption of mass timber, and increased investor and consumer awareness.
Click on the subscribe button below to receive more ESG insights from our investor blog series.
Sources:
[1] Dunn, Katherine. “From concrete to steel, how construction makes up the ‘last mile’ of decarbonization”. Fortune. February 16, 2021. Accessed December 15, 2021. https://fortune.com/2021/02/16/concrete-steel-construction-design-climate/
[2] Robinson, Graham et al. “Future of Construction”. Oxford Economics. September 2021. Accessed December 15, 2021. https://www.marsh.com/content/dam/marsh/Documents/PDF/it/it/The_Future_of_Construction_ExecSum_2021.pdf
[3] Newcomer, Reed. “Seven Benefits of Panelized Mass Timber”. Morrison-Maierle. November 3, 2021. Accessed December 10, 2021. https://m-m.net/seven-benefits-of-panelized-mass-timber/
[4] United Nations “UN chief promotes 'enormous' benefits of greener cities”. UN News. October 3, 2021. Accessed December 10, 2021. https://news.un.org/en/story/2021/10/1101992
[5] Industrialized Wood-Based Construction Conference “Mass Timber Changes the Face of Construction in Europe”. September 24, 2020. Accessed December 9, 2021. https://www.iwbcc.com/mass-timber-changes-the-face-of-construction-in-europe/
[6] LPA Design “An Office Made of Wood”. March 23, 2021. Accessed December 8, 2021. https://lpadesignstudios.com/catalyst/an-office-made-of-wood
[7] Forest2Market “Everything You Wanted to Know About CLT”. March 15, 2021. Accessed December 9, 2021. https://www.forest2market.com/blog/everything-you-wanted-to-know-about-clt
[8] Stahl, Nicole Zaro. “Mass Timber Moves Mainstream”. Tradeline. December 2, 2020. Accessed December 9, 2021. https://www.tradelineinc.com/reports/2020-11/mass-timber-moves-mainstream
[9] Parker Smith & Feek. “The Proliferation and Risk Considerations of Mass Timber”. July 29, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2021. https://www.psfinc.com/articles/proliferation-and-risk-considerations-of-mass-timber/
[10] Think Wood “4 Things to Know About Mass Timber”. 2021. Accessed December 10, 2021. https://www.thinkwood.com/blog/4-things-to-know-about-mass-timber
[11] Bland, Kenneth. “Tall Mass Timber Buildings Now Possible Under 2021 IBC Code Changes”. Construction Executive. January 7, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2021. https://www.constructionexec.com/article/tall-mass-timber-buildings-now-possible-under-2021-ibc-code-changes#:~:text=Tall%20Mass%20Timber%20Buildings%20Now%20Possible%20Under%202021%20IBC%20Code%20Changes,-By%20Kenneth%20Bland&text=The%20International%20Code%20Council%20(ICC,buildings%20up%20to%2018%20stories.
[12] Stahl, Nicole Zaro. “Mass Timber Moves Mainstream”. Tradeline. December 2, 2020. Accessed December 9, 2021. https://www.tradelineinc.com/reports/2020-11/mass-timber-moves-mainstream
[13] FAO and UNEP. 2020. The State of the World’s Forests 2020. Forests, biodiversity and people. Rome. Accessed December 11, 2021. https://doi.org/10.4060/ca8642en
[14] Amsterdam Institute for Advanced Metropolitan Solutions. “Building in timber is bad for the environment. Fact or fiction?”. November 25, 2021. Accessed December 12, 2021. https://www.ams-institute.org/news/timber-construction-bad-environment-and-forests-fact-or-fiction/
[15] Think Wood. “10 Questions with Sustainable Forestry Expert, Dr. Edie Sonne Hall”. Accessed December 12, 2021. https://www.thinkwood.com/blog/10-questions-with-sustainable-forestry-expert-dr-edie-sonne-hall
[16] Dalheim, Robert. “World's tallest timber tower begins overtaking nearby buildings”. Woodworking Industry News. June 22, 2021. Accessed December 13, 2021. https://www.woodworkingnetwork.com/news/woodworking-industry-news/worlds-tallest-timber-tower-begins-overtaking-nearby-buildings
[17] Think Wood. “First Mass Timber Overbuild Differentiates in Washington D.C.” GB&D. April 23, 2021. Accessed December 14, 2021. https://gbdmagazine.com/first-mass-timber-overbuild-differentiates-in-dc/?_ga=2.63940524.2064245365.1638468663-649446769.1638468663
[18] Heilmeyer, Florian. “In Sweden, the Sara Kulturhus Expands the Possibilities of Mass Timber”. Metropolis. December 14, 2021. Accessed December 15, 2021. https://metropolismag.com/projects/sara-kulturhus-mass-timber/
[19] UN Environment Programme. “The Six-sector solution to the climate crisis”. United Nations. Accessed December 13, 2021. https://www.unep.org/interactive/six-sector-solution-climate-change/




