Knowing how exposed and how well your portfolio companies manage their material ESG issues is a critical part of making well-informed investment decisions.
That is why the world's leading investors rely on our ESG research and ratings for a consistent approach to evaluate financially material ESG issues that affect the long-term performance of their investments.
Covering more than 16,000 companies, Morningstar Sustainalytics has the widest coverage of analyst-based ESG Risk Ratings in the market. The newly expanded universe includes public and private companies, fixed-income issuers and listed Chinese companies and allows investors to support diversified investment strategies.
Learn more about why Sustainalytics’ ESG Research and Ratings are the industry standard.
Gain valuable insights on the potential economic and societal benefits of aligning with ESG standards, as well as the potential costs and disruptions.
Latest Insights
Child Labor in Cocoa Supply Chains: Unveiling the Layers of Human Rights Challenges
ESG in Conversation: The AI Revolution Comes to ESG
Morningstar Sustainalytics Expands ESG Risk Ratings Coverage to Fixed Income, Private Equity, and China
Morningstar Sustainalytics' ESG Risk Ratings
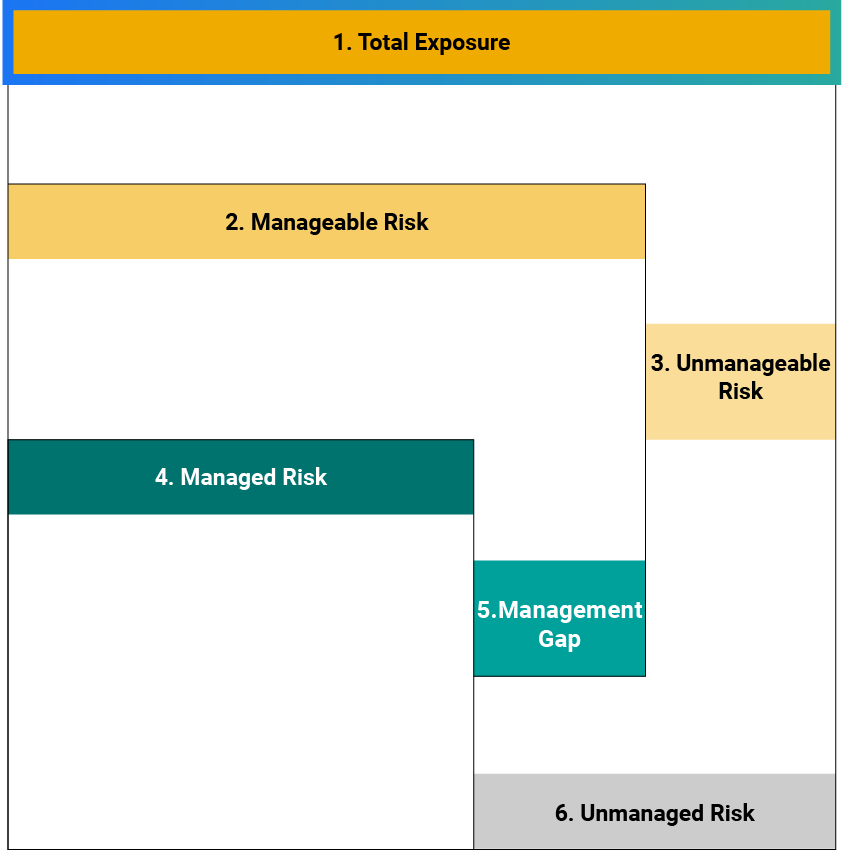
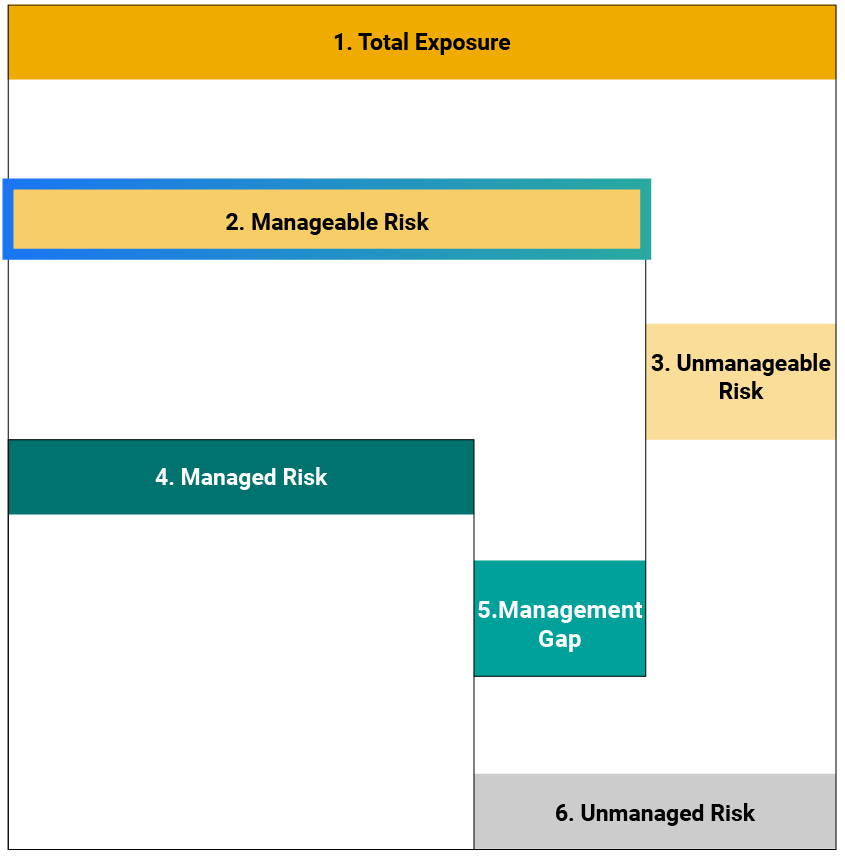
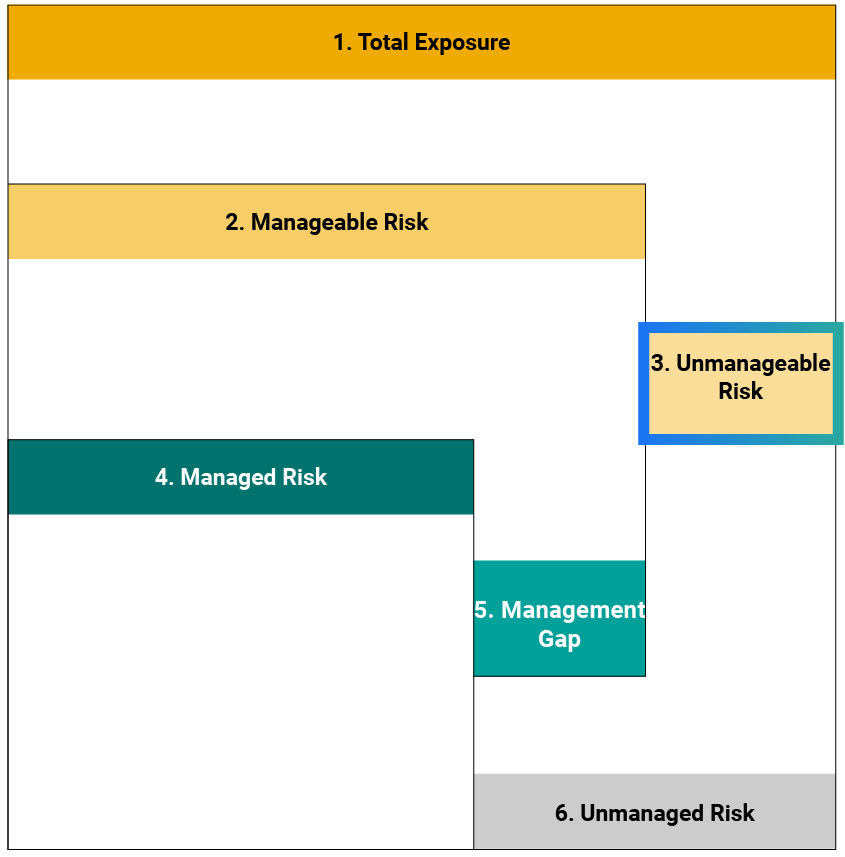
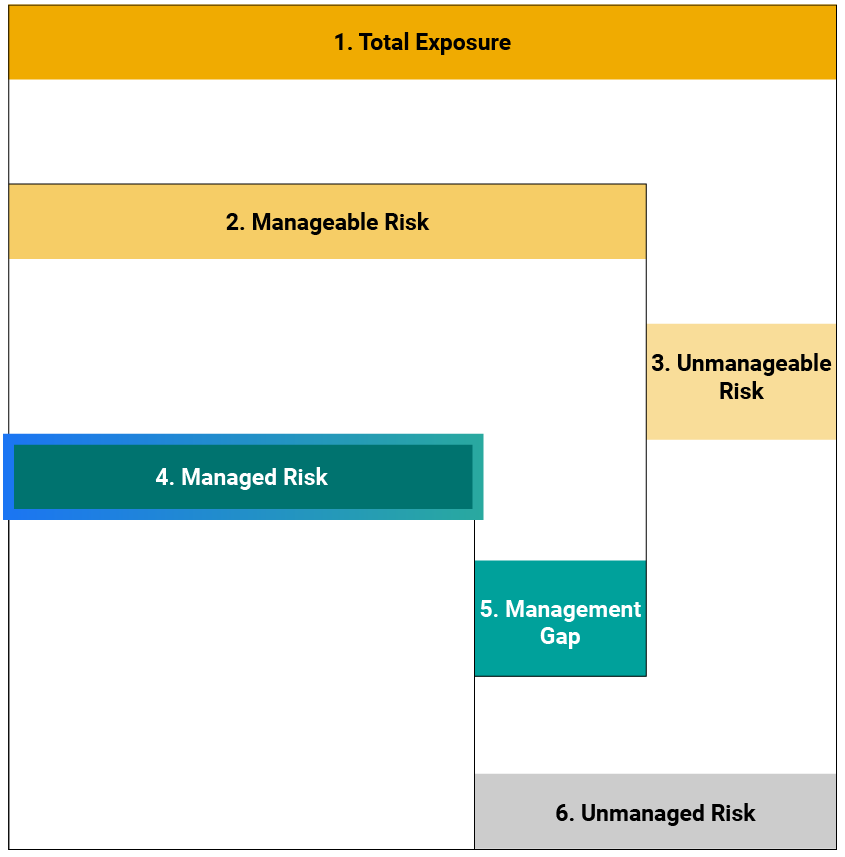
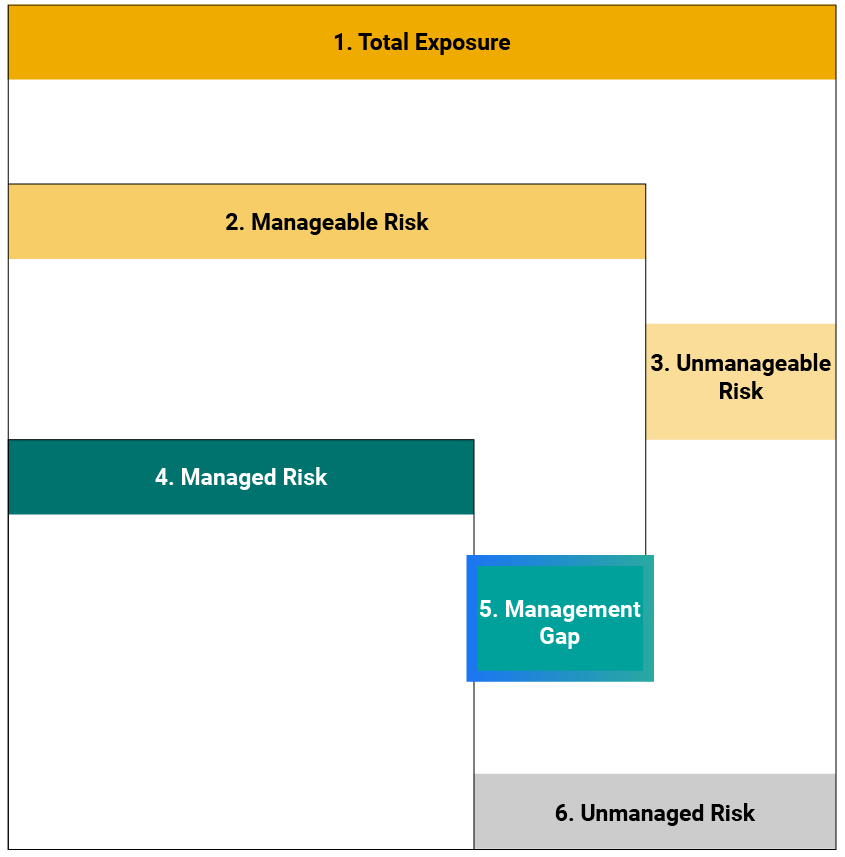
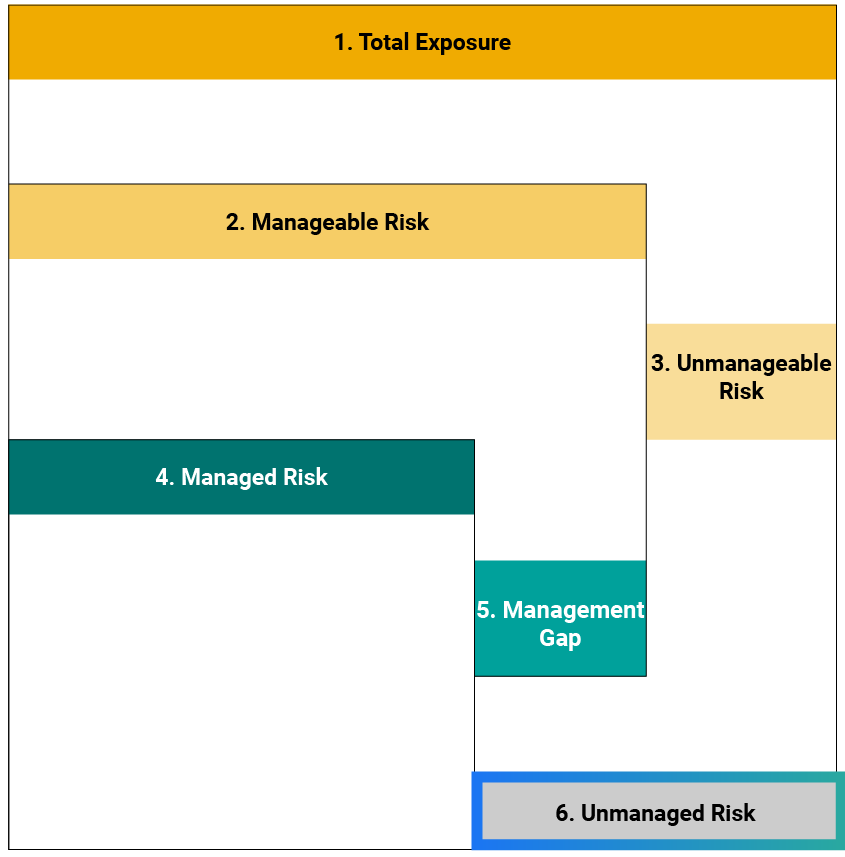
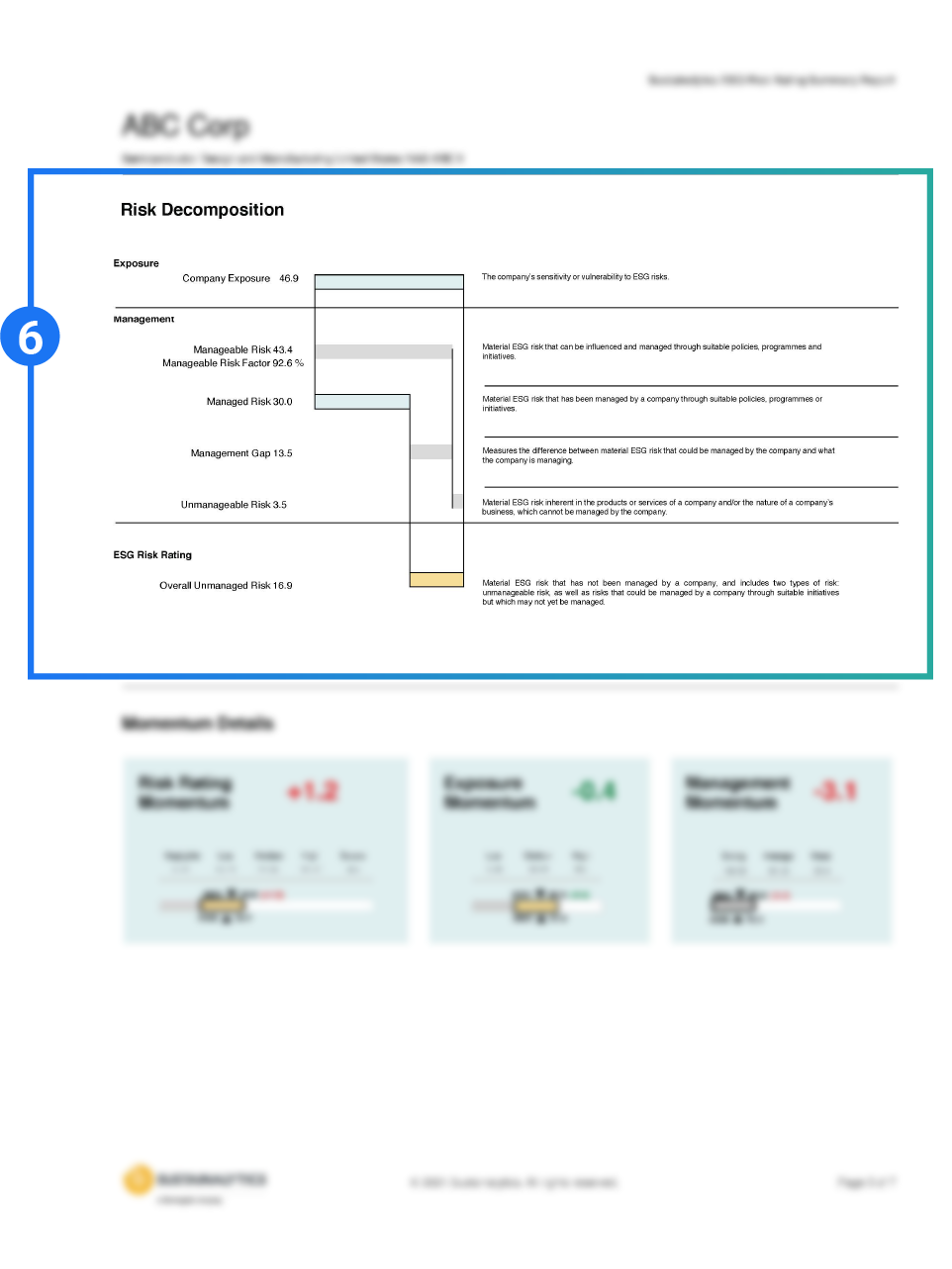
Sustainalytics’ ESG Risk Ratings measure a company’s exposure to industry-specific material ESG risks and how well a company is managing those risks. This multi-dimensional way of measuring ESG risk combines the concepts of management and exposure to arrive at an absolute assessment of ESG risk. We identify five categories of ESG risk severity that could impact a company’s enterprise value

The Rigor and Comprehensiveness that the World’s Leading Investors Count On
Absolute Measure of ESG Risk
A sophisticated methodology for rating absolute ESG risk, while enabling best-in-class analysis. Company ratings are comparable across peers and subindustries and allow for easy aggregation at the portfolio level.
Extensive Coverage
The ESG Risk Ratings research universe includes more than 16,300 analyst-based ESG Risk Ratings, spanning public equity, fixed-income, and privately held companies. Additionally, the universe has enhanced coverage of Chinese companies listed in Shanghai and Shenzhen, which are predominant regional contributors in emerging market indices.
Integrated Corporate Governance Information
Fully integrated, comprehensive corporate governance research and ratings.
Transparent Methodology
Transparent methodology with multiple levels of data and qualitative insights to provide clients with custom ESG solutions.
Two-Dimensional Materiality Framework
Two-dimensional materiality framework measures a company’s exposure to industry-specific material risks and how well a company is managing those risks.
Three Central Building Blocks
Corporate governance, material ESG issues, and idiosyncratic issues (black swans) form the three central building blocks of our ESG research and ratings.
Five Risk Levels
The ESG Risk Ratings are categorized across five risk levels: negligible (0-10), low (10-20), medium (20-30), high (30-40) and severe (40+).
16,000+ Companies Covered
Sustainalytics' ESG Research and Ratings span more than 16,000 companies and encompass most major global indices.
20 Material ESG Issues
The ratings framework is supported by 20 material ESG issues that are underpinned by more than 300 indicators and 1,300 data points.
Flexible Accessibility
The ESG Risk Ratings are available through Global Access, Datafeeds and API as well as several third-party distribution platforms.
Human Insights Supported by AI Efficiency
Daily News Monitoring
AI-powered Digital Content Curation
Research analysts leverage smart technologies to enable them to monitor more than 60,000 media sources, and up to one million news articles daily.
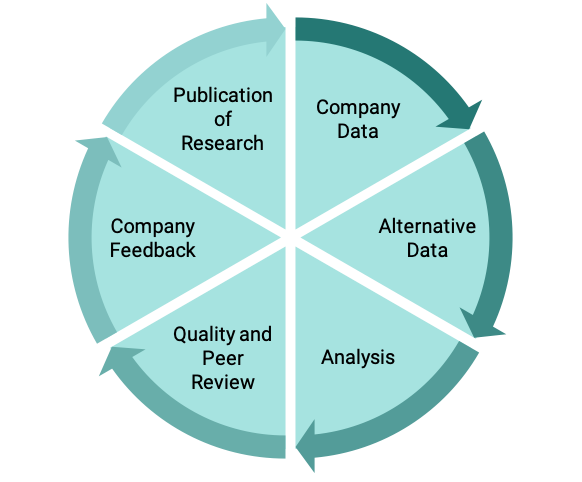
Robust Annual Update Cycle
- Company profiles updated annually with corporate reporting cycle
- Alternative data sources, like regulatory filings on product recalls and NGO sources, augment self-reported corporate data
- Analysis by a team of over 800 ESG research analysts supported by artificial intelligence powered descriptive and predictive analytic capabilities
- Robust quality control mechanisms with peer reviews by senior analysts and company feedback mechanisms
About Our Framework
Investor Use Cases
ESG Integration
Multi-dimensional ESG risk scores can be incorporated into equity or bond valuation models and aggregated at the portfolio-level.
Best-in-Class Investment Analysis
Comparable company scores support flexible applications for best-in-class analysis, including subindustry, sector or regional approaches.
Screening and Benchmarking
Overall Risk Ratings and material ESG issue scores support risk-based ESG screens and enable robust benchmarking across and within sectors and subindustries.
Thematic Investing
Scores on material ESG issues support thematic investment themes and provide meaningful new input for fund and index creation.
Engagement and Voting
Material ESG issue framework effectively supports engagement with companies on priority ESG issues and informs voting decisions on E&S shareholder resolutions.
Reporting & Promotion
Communicate sustainability performance and commitment through ESG reporting and leverage the Morningstar Sustainability RatingTM for funds for marketing purposes.
Report Insights
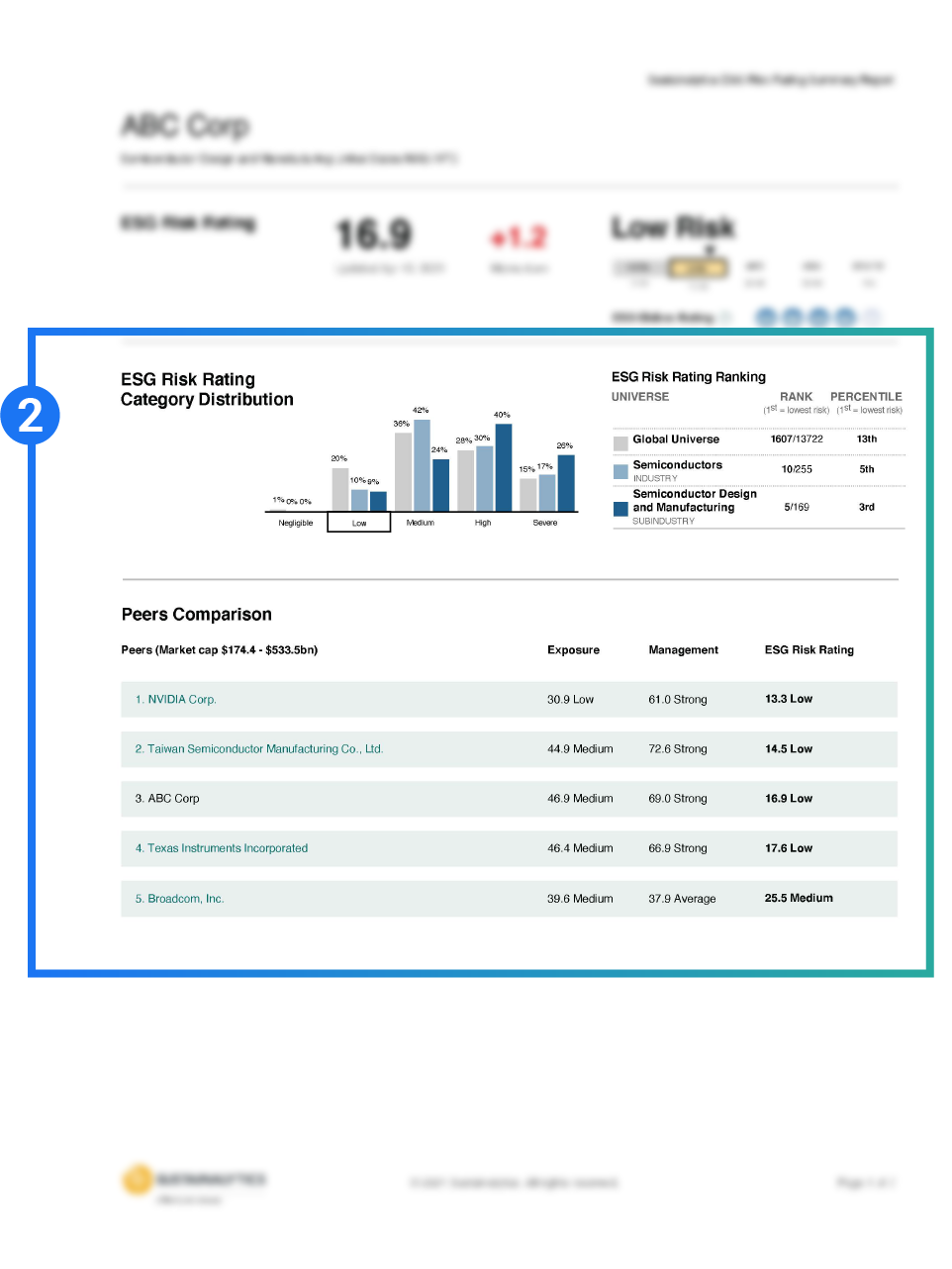
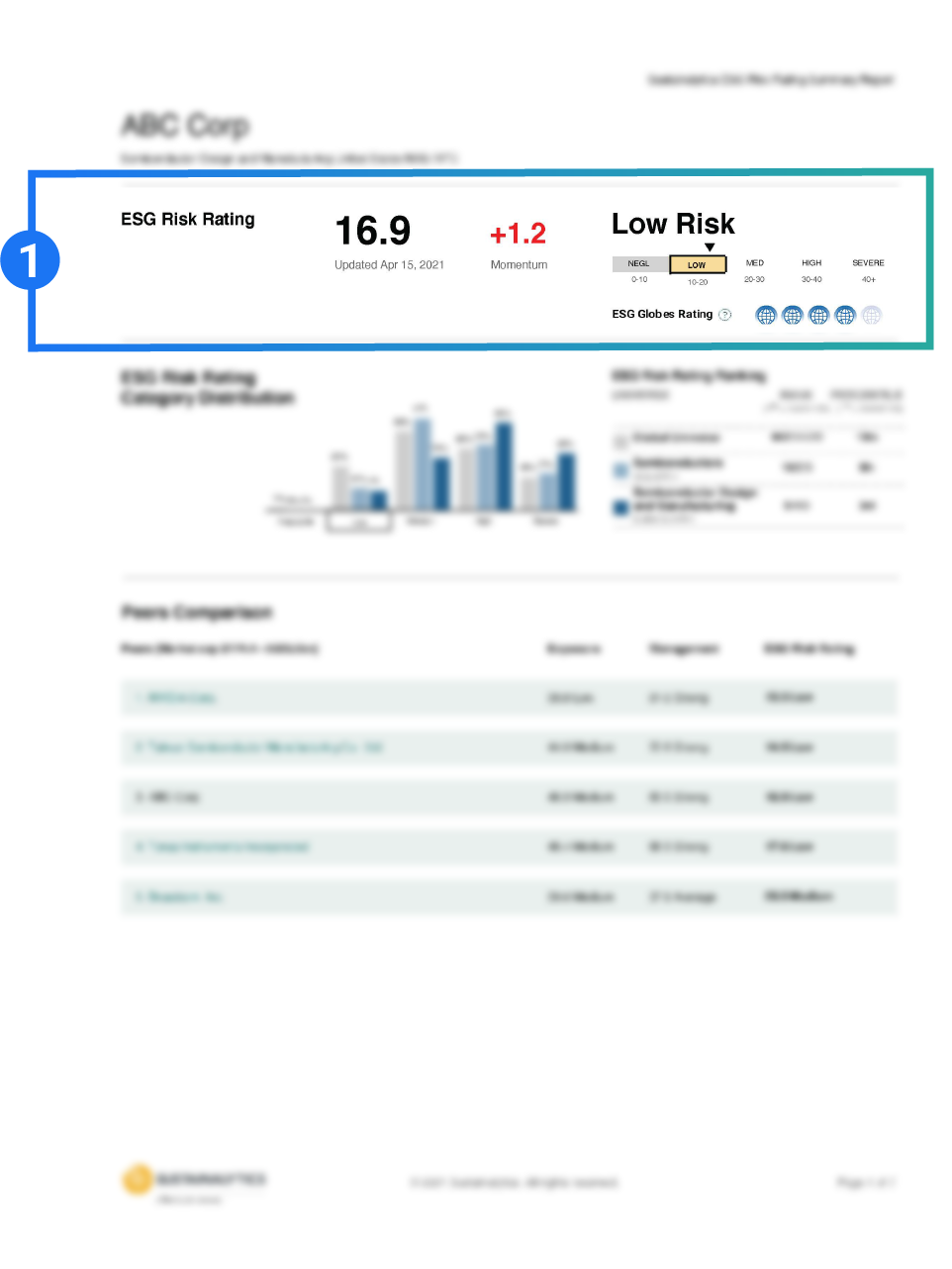
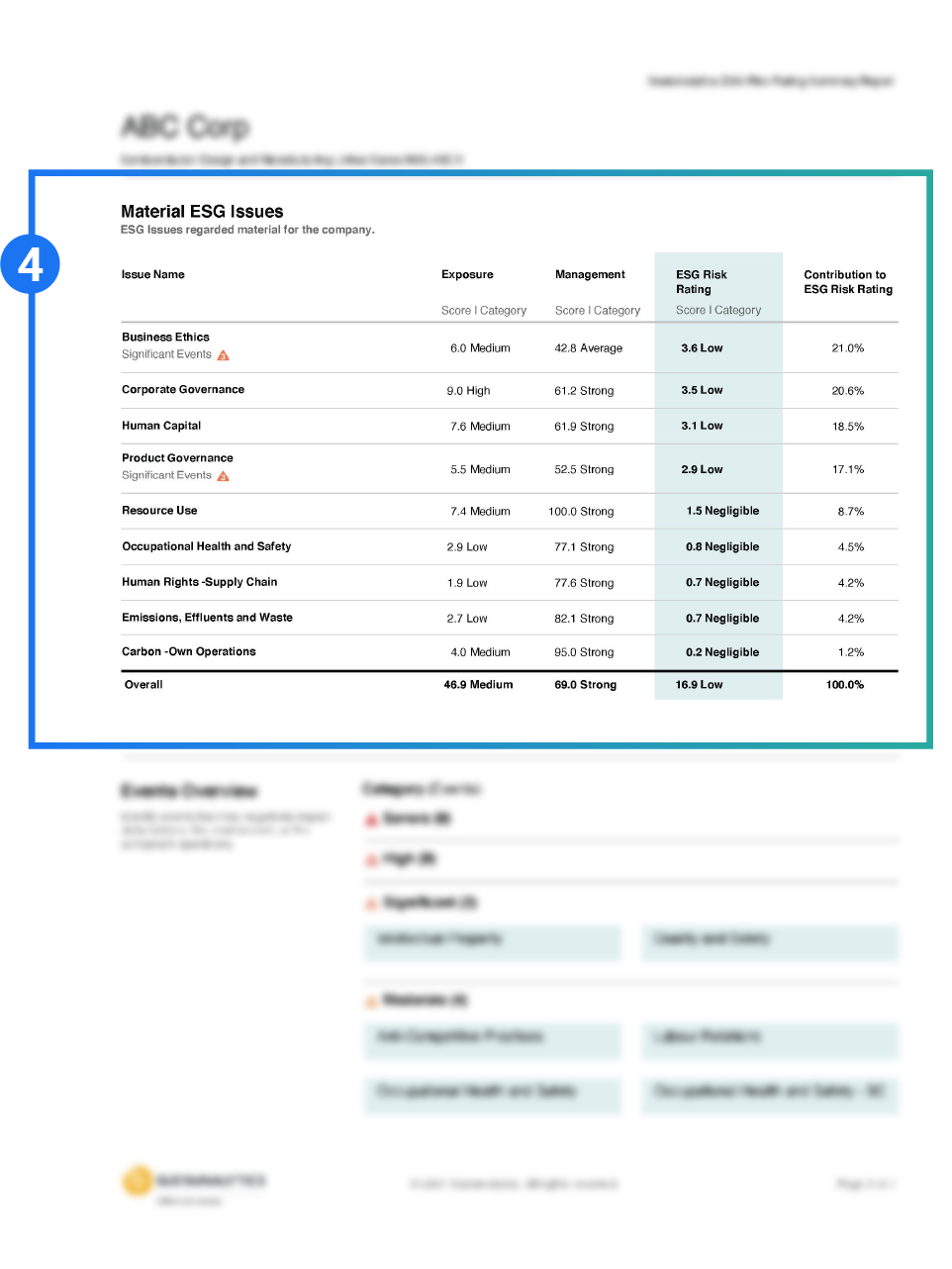
Company ratings are categorized across five risk levels: negligible, low, medium, high, and severe and represented by our ESG Globes icons.
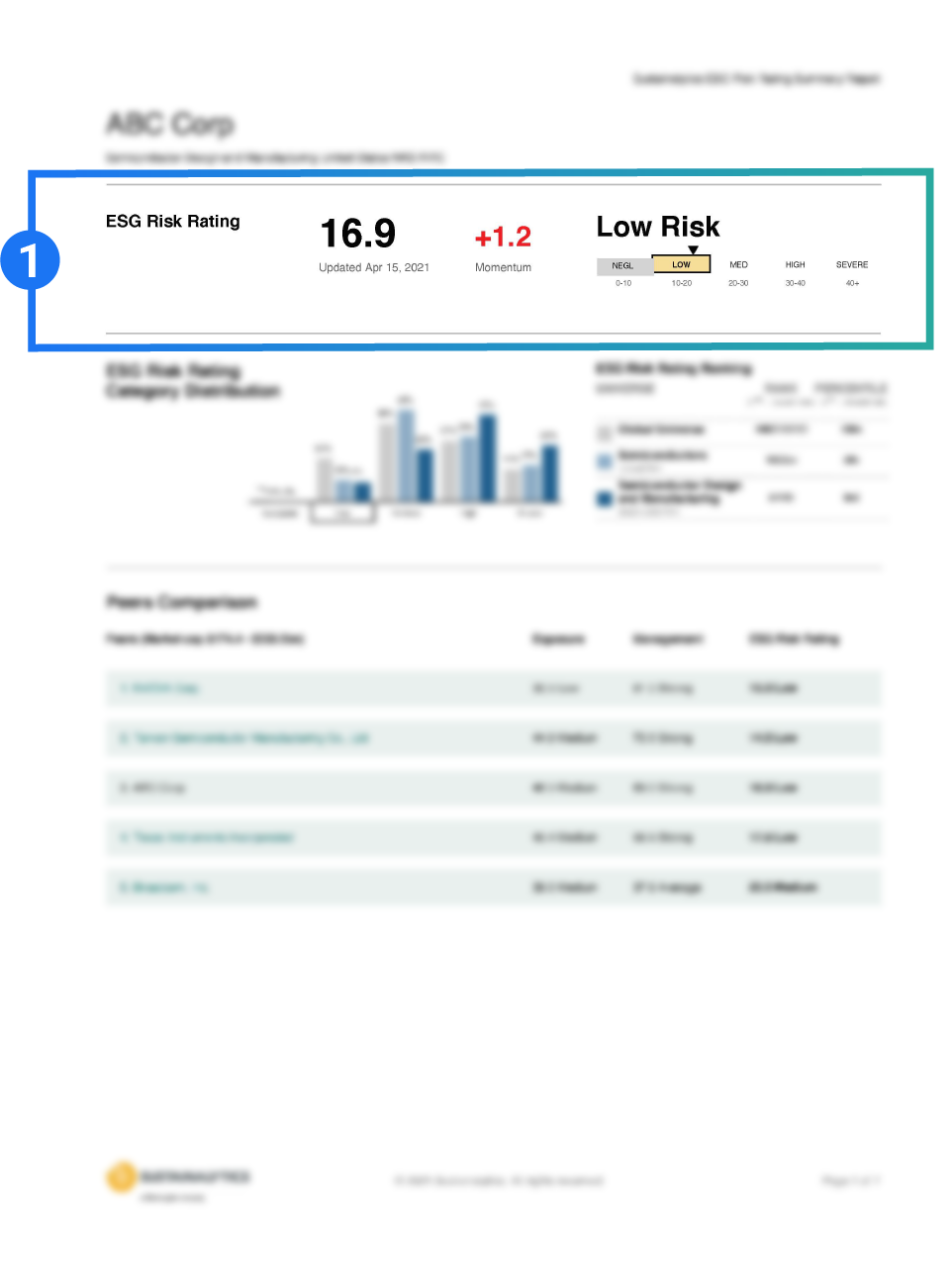
A company’s risk is measured against its industry peers and against the global universe.
Qualitative analysis, underpinned by analyst insights and quantitative data, describes the reasons why a company is exposed to specific material ESG issues and explains how well a company is managing these issues.

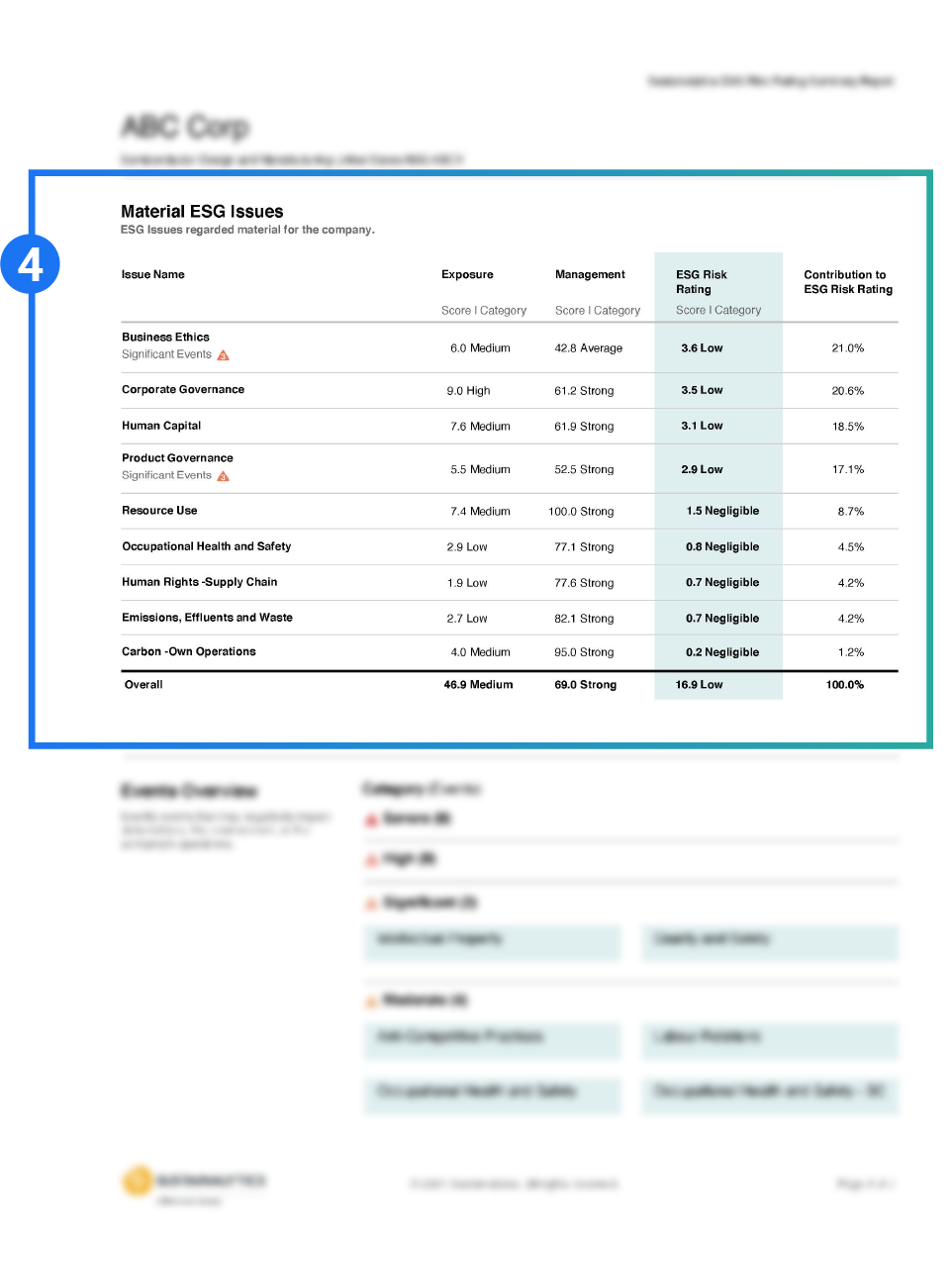
Material ESG Issues (MEIs) are identified and brought into focus.
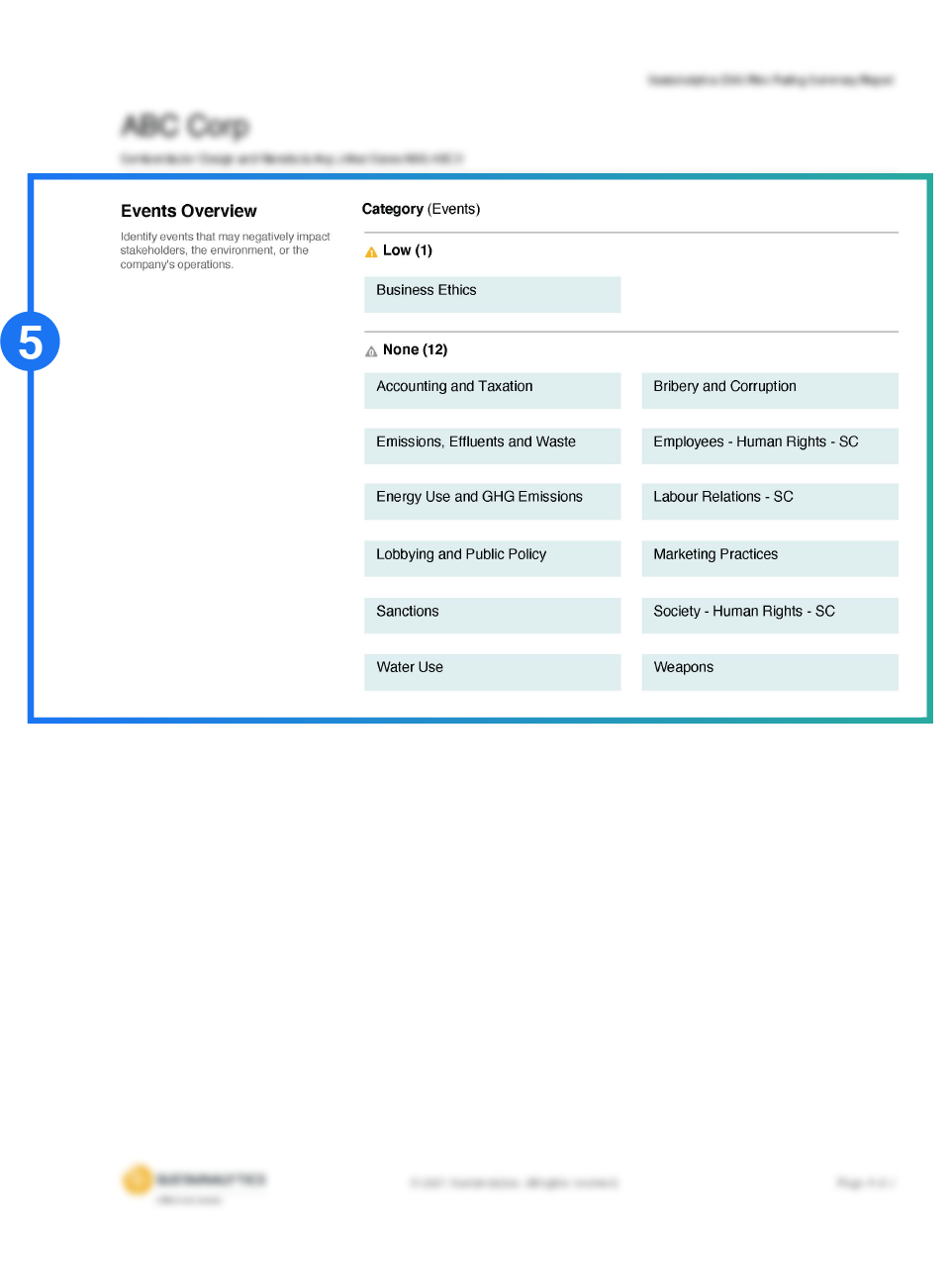
Transparency into company events that may impact a company’s operations, stakeholders or the environment.
The magnitude to which a company is exposed to ESG risk and how well the company is managing that risk is measured and explained.




Why Sustainalytics?
A Single Market Standard
Consistent approach to ESG assessments across the investment spectrum.
Award-Winning Research and Data
Firm recognized as Best ESG Research and Data Provider by Environmental Finance and Investment Week.
End-to-End ESG Solutions
ESG products and services that serve the entire investment value chain.
30 Years of ESG Expertise
800+ ESG research analysts across our global offices.
A Leading SPO Provider
As recognized by Environmental Finance and the Climate Bonds Initiative.

Climate Solutions
Identify and manage investment risks and opportunities with climate research, ratings and data for investors.
Learn More
Material Risk Engagement
Engage on the most material ESG risks identified by the ESG Risk Ratings.
Learn More
Impact Solutions
Measure, manage and report on the social and environmental impact of your portfolio.
Learn MoreMorningstar® Global Market SustainabilitySM Index Family
Best-in-class equity index that features reduced ESG risk profile with low to moderate tracking error.
Morningstar® Sustainability Dividend Yield FocusSM Index Family
High Income generating equity investments focused on total returns with reduced ESG Risk.
Morningstar® Global Corporate Bond Sustainability IndexesSM
Diversified corporate bond portfolio that avoids bonds with high ESG risk relative to their sector peers.
Morningstar® Sustainability Moat IndexesSM
Exposure to companies that have distinct competitive advantages as well as low ESG Risk.
Related Insights and Resources
Navigating the EU Regulation on Deforestation-Free Products: 5 Key EUDR Questions Answered About Company Readiness and Investor Risk
The EUDR comes into effect in December 2024, marking an important step in tackling deforestation. In this article, we answer five key questions who the EUDR applies to, how companies are meeting the requirements, and the risks non-compliance poses to both companies and investors
Child Labor in Cocoa Supply Chains: Unveiling the Layers of Human Rights Challenges
Child labor remains a persistent issue in the cocoa supply chain. So can major food brands do to stop it? Discover the steps companies can take to address the issue and ways investors can engage with companies to mitigate it.
The Raw Materials Crunch: Industry Risks Due to Physical Scarcity, Supply Concentration and Intense Demand
As demand for critical raw materials increases, due in part to the low-carbon transition, industries reliant on those materials face growing risks. In this article, discover what’s driving those risks.
-5-key-questions-answered-about-company-readiness-and-investor-risk.tmb-thumbnl_rc.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=ee2857a6_2)