Climate Change, Innovation, and Cybersecurity in the Defense Industry: New Opportunities for ESG Investors
While perhaps not a widely considered link between the defense industry and climate change, several Eurosatory conference sessions addressed how climate change can intensify security risks and threats.
Telecom Network Outages, the ESG Risks of a Connected World
The telecom industry is exposed to several Material ESG Issues, including Data Privacy and Security, Business Ethics, Human Capital and Product Governance. Product Governance issues in the telecom industry include service quality, maintaining reliable, high-speed networks, and responding to customer billing concerns.
ESG Risks Affecting Data Centers: Why Water Resource Use Matters to Investors
Data centers play a critical role for many technology and telecom companies and for their supporting servers, digital storage equipment and network infrastructure for data processing and storage. Data centers require high volumes of water directly for cooling purposes and indirectly, through electricity generation. Morningstar Sustainalytics’ recent activation of the Resource Use Material ESG Issue (MEI) within its ESG Risk Ratings recognizes water risks of data centers.
Looking at ESG in Crypto, Blockchain, and Public Equities
Beyond the volatile crypto market, blockchain has several features that lend well to commercial applications. Blockchain can help improve the transparency, speed and efficiency of data transfers and monetary transactions. Businesses in multiple industries are using blockchain tools to enhance payment platforms and secure supply chain management systems. Sustainalytics’ latest Thematic Research report, An ESG Lens on Blockchain and Public Equities, surveys ESG risks and opportunities related to applications of blockchain technology that are being developed by listed companies across multiple sectors of the economy.
North American Material Risk Engagement Trends: ESG Reporting Frameworks, Emission Reduction Targets and Beyond
There are many factors that rating agencies consider within its overall assessment. For example, ESG rating companies tend to look for at least three years of ESG metrics to determine company trends and long-term ESG targets, goals, and strategies to manage and reduce ESG risks at least five years ahead. Read on to learn about how Sustainalytics' Material Risk Engagement program promotes and protects long-term value by engaging with high-risk companies on financially-material ESG issues. (A North American Snapshot)
Antitrust in the Digital Age
On July 27th, the chief executives of four (Alphabet, Amazon, Apple and Facebook) of the world’s most prominent technology companies will appear before the US Congress as part of an ongoing antitrust investigation into their market power.[i] This is the latest in a series of developments that includes federal and state-level investigations in the US into the market practices of these companies. Back in 2018, as part of Sustainalytics publication, ESG Risks on the Horizon, our team had noted that the antitrust related scrutiny of major technology companies is likely to persist given the market concentration these companies had established within the digital economy. While there is significant uncertainty as to the ultimate regulatory response, given the outsized position of these four companies in the S&P 500 and sustainability indices, this type of regulatory and market scrutiny is an area that is important for investors to examine in terms of long-term risks to the enterprise value of these companies.
5G and Industry 4.0: Enabling Efficient and Resilient Infrastructure
There is significant hype associated with the rollout of 5G networks, which is largely tied to the incredible data transfer speeds 5G capable networks can offer. However, speed is only part of the equation. Beyond speed, key attributes of 5G also include lower latency, reduced cost per gigabyte and larger connection volumes. 5G, unlike previous network technology, will be software-defined, enabling networking functionality to be flexible and adaptable over time.[i] As a result, 5G is anticipated to create a new digital backbone to power future infrastructure needs – a topic we explored in Sustainalytics’ report, 10 for 2020: Creating Impact Through Thematic Investing.
Coronavirus: Flattening the Misinformation Curve
In February 2020, the WHO Director-General Tedros Ghebreyesus said misinformation about COVID-19 is just as dangerous as the virus itself. “We are not just fighting an epidemic; we are fighting an ‘infodemic.’ Fake news spreads faster and more easily than the virus and is just as dangerous.”[i]
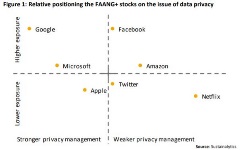
Managing data privacy risk: comparing the FAANG+ stocks
Collecting and processing personal data has become one of the most significant drivers of financial value in today’s economy. But as the upside of personal data grows, so too does the downside risk associated with data security, management and privacy.
Cybersecurity: A Pervasive Risk
In 2017, in the wake of the WannaCry ransomware attack, we argued that the event should be seen as a cybersecurity wake up call. Since then, cybersecurity risks have remained a source of uncertainty for most companies, driven by the increasing intensity, both in volume and impact, of cyberattacks. These risks are compounded by the continuous expansion of critical infrastructure (energy grids, utilities, hospitals) to digital platforms and the breadth of sensitive information that is housed in online servers. As a result, the pool of lucrative targets for malicious actors continues to grow. This is reflected in the notable rise in the number cyber insurance claims. According to a study by AIG, 2018 had the same number of cyber insurance claims as the preceding two years combined.[i]
China’s Millennials and ESG
A country’s demographics has a strong influence on long-term social trends, including the development of ESG issues. With millennials becoming the dominant cohort among the workforce and consumers, we are witnessing the social transformations that come with a new generation. Although occurring globally, these transformations are particularly dramatic in China, due to the contrasting social environments experienced by China’s millennials and their parents.